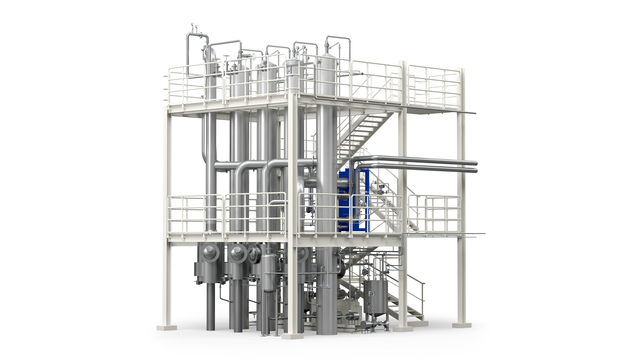
FilmVap
Esses evaporadores podem processar líquidos claros e não incrustantes, assim como líquidos moderadamente incrustantes.
Liquid distribution, the key element
The liquid distributor is the most critical component in any falling-film evaporator. The optimized design of the liquid distributor helps prolong uptime and reduce CIP costs. It also reduces any additional effluent generation stemming from CIP, as well as the treatment costs involved.
Platter distributor
The combination of uniform distribution of liquid in a platter distributor and adequate wetting helps to avoid inefficient distribution and significantly reduces fouling in the tubes. The vent tubes maintain pressure equilibrium above and below the distributor plate as well as maintaining a consistent static weight of liquid on the distribution plate.
Jet distributor
 Another type of liquid distributor available in Alfa Laval FilmVap evaporators is the jet distributor, fitted with solid cone spray nozzles. The size and quantity of these nozzles depend on the liquid flow and the tube sheet diameter in the heat exchanger. The larger hole size compared with a platter distributor reduces the risk of blocking the nozzle and ensures even distribution to the tubes.
Another type of liquid distributor available in Alfa Laval FilmVap evaporators is the jet distributor, fitted with solid cone spray nozzles. The size and quantity of these nozzles depend on the liquid flow and the tube sheet diameter in the heat exchanger. The larger hole size compared with a platter distributor reduces the risk of blocking the nozzle and ensures even distribution to the tubes.
Benefits
- Small footprint
- Superior distribution
- Reliable and robust
Como funciona
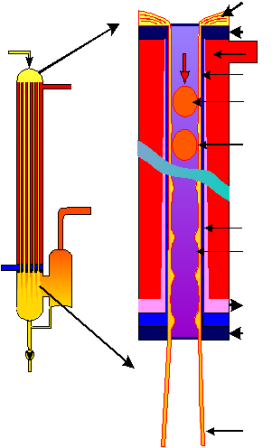 Alfa Laval’s FilmVap evaporation systems are based on tubular falling film principle. The product is fed at the top of the evaporator. Via a liquid distribution system, the product enters the tubes where it forms a film along the inside wall.
Alfa Laval’s FilmVap evaporation systems are based on tubular falling film principle. The product is fed at the top of the evaporator. Via a liquid distribution system, the product enters the tubes where it forms a film along the inside wall.
Steam is applied as a source of heat on the outside of the tubes. As boiling occurs, the film under gravity and accelerated by the produced vapour falls to the bottom of the tube, where the mixture of vapour and concentrate product enters the separation stage.
Vacuum is applied in the FilmVap system to decrease the boiling temperature. The vacuum is created by condensing the vapour from the last effect in a condenser, e.g. the highly efficient and compact AlfaCond condenser. A vacuum pump is normally used to remove the non-condensable gases.
By designing with multiple effects, the steam consumption in evaporation systems is reduced: the vapour produced in one effect is used as heating media in the subsequent effect. In combination with thermal vapour recompression and/or mechanical vapour recompression, the steam consumption can be reduced to only a fraction of the evaporation capacity.